In this blog, we will cover the contents of the various types of security attacks, also briefly explain the ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) Spoofing attack, and many more.
Introduction
The Internet has been one of the most important and crucial needs of people in this rapidly
growing world of modernization.
As its importance is growing day by day different
types of vulnerabilities and security attacks are also getting high which has become
a major issue on the internet.
The Internet plays a major role in keeping communication
going through different sites and sources, many people perform different smooth
operations and activities with the help of the internet and keep their sensitive information
and data on the internet but as we all know that internet is not fully trustable and
reliable and have different types of malware and vulnerabilities occurs due to which
different attackers and hackers gain access through people sensitive, financial and
personal data which will be the major advantage for the attackers and the huge loss
for the owner.
Different types of cyber-attacks have been emerging rapidly which has
become a severe problem and one of the main attacks among them is ARP
Spoofing.
ARP Spoofing
ARP Spoofing is a vulnerable type of attack that has become one of the major
problems in the local area network (LAN) and it leads to various other harmful
attacks.
It is a malicious attack that sends falsified ARP messages over a LAN and
leads to the associated linking of an attacker’s MAC address with the IP address of a legitimate computer or server on the network.
It is generally a technique used by
attackers to perform cache poisoning by putting incorrect IP to MAC address
mappings in the victim’s ARP cache.
It is divided into two forms namely that is request
attack and response attack.
In the request attack, the attackers transmit an ARP
request message with a fake source IP-MAC in the ARP header.
When the receiver
receives the spoofed ARP message the ARP cache table gets updated with the
attacker’s fake IP-MAC pair.
After that when the victim sends its subsequent packets
to the fake IP, the packets will be destined to the MAC of the host created or
generated by the attacker in the fake IP-MAC pair.
In this way, the attacker can
change or deny the traffic sent to a user in the network.
In the case of a response
attack, the attackers will either respond to normal ARP request with fake ARP replies
that map the next-hop IP to the attacker's MAC address or sends spoofed ARP
replies without having the issue of a request.
There are generally different types of attacks launched by ARP spoofing due to
which severe harm can be caused to the LAN.
The different types of ARP attacks
carried out by ARP spoofing to create different vulnerabilities are listed
below:
Types of Attacks
Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack
Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack is an active eavesdropping technique.
Here a
hacker exploits ARP Cache Poisoning to capture network traffic between two nodes.
In this case, if a communication session between two devices X and Y is going on
then the attacker fakes X by pretending to be Y. It means that whenever X tries to
send information to Y, it actually sends information to the attacker who can change
and modify the information according to the attacker and forwards the information to
Y to keep the communication going on. The attacker can go through all the
sensitive information and data and can change/modify them before forwarding the
data to Y.
The hacker can capture all the network traffic and can also sniff
passwords or hijack the secured Internet Sessions.
This type of attack is also known
as “Bucket Bridge Attack”, “Fire Brigade Attack”, “Monkey in the Middle Attack”
etc.
Denial Of Service (DOS) attack
It is a type of attack on a networking structure where it disables a server from
servicing its clients.
It attempts to slow down the server by sending millions of
requests and also creates flooding on a server with large packets of invalid data or
sending requests with an invalid or spoofed IP address.
In this type of attack, the
attacker will prevent the two communicating hosts from getting connected to each
other.
The malicious machines create a large number of unknown or fake identities
which is it makes system resources unreachable to its intended users.
The attack
soaks the target machine with outward communications requests and the server
cannot get respond to authentic traffic.
The response comes so slowly that it is like
not responding at all.
Connection Hijacking
Packet or Connection Hijacking is a type of method where connected nodes can be
victimized into getting their connection changed and taking full access to it; it allows an attacker to take control of the connection between two
computers.
This type of attack uses ARP poisoning to steal sessions IDs and
allows the attackers to get access to private systems and data connection hijacking.
This type of attack is usually performed to attack the social network website, and
banking websites to gain access to the websites and valid information
provided from that site.
It plays a major role in stealing the confidential and sensitive
information which passes through the network. It can steal and
capture messages without the knowledge of the senders.
The big advantage of
this type of attack is that it does not have to break any defense or security firewalls, it
just has to keep listening over the network and can take control of any type of valid
sessions over them.
Cloning
MAC addresses were meant to be globally unique identifiers for every network
interface which were burned into the ROM of each interface and could not be
changed.
But nowadays, MAC addresses can easily be changed without spoofing the
software, by using a single variable to “ifconfig”, the interface configuration program
for the O.S.
An attacker could DOS a target computer, then assigns themselves as the IP and MAC of the target computer and collects all the frames and sensitive
information for the target as they wanted to do. This is the process involved in
cloning.
The main reason for performing an ARP spoofing attack is to intercept data frames on a
network, modify the traffic and stop all the traffic.
It is one of those attacks that can
be performed easily without any type of difficulties or disruptions.
It can damage
and take information secretly without the knowledge of the user due to which it can be
taken as one of the most dangerous attacks.
The current scenario of ARP spoofing is
not dangerous as before because different types of tools and resources are being
implemented to control the attack but as we all know that “Everything is not perfect”,
different types of holes and improper functions are still there due to which the tools
and resources also cannot completely avoid the attacks properly.
Background
Address Resolution Protocol is also known as ARP is a stateless protocol and one of
the most popular communication protocols in the local area network (LAN)which lies
under the network layer on an open system interconnections (OSI) model.
It is one of the
most important protocols in Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)/Internet Protocol
(IP) and is used to associate the IP address of the network layer to the MAC address
of the data link layer.
With the help of this protocol, the total number of hosts
connected to the LAN can be identified and several MAC addresses to IP addresses
can also be discovered, in a LAN environment.
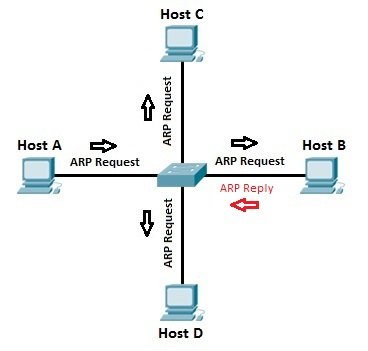
ARP is performed by sending a message request called broadcast to get the MAC to address the IP
address.
While carrying out the operations each device in the network receives the
message and compares it with its IP address and if there is a match between the
IPs then the generated ARP will be known as unicast and the other devices which
are identified and do not match the IP’s then such packets will be dropped
immediately.
After that, the IP-MAC address is stored in the ARP cache table of any
network host. The main weakness of ARP is that it is not designed with security
features and it lacks the features of authentication and integrity and does not support
it due to which it can easily be exploited and different hackers and attackers can go through the sensitive data and information which will be great loss and harm.
ARP
can easily be spoofed due to which it is highly susceptible to spoof and poison
attacks.
ARP Spoofing is an OSI Layer 2 attack that exploits the statelessness and
vulnerability of the protocol and makes network hosts susceptible to different issues
and generates serious outcomes for any user.
These types of attacks are performed
to take important information and empower destructive gathering to catch, alter or
even stop the information exactly anytime even if it is in the way of traveling to its
destination.
An ARP poisoning is a kind of hacking technique and is carried out when an attacker
sends a fake ARP request or ARP reply to the LAN which leads to a change in the ARP
cache table that is connected with the host IP address to the attacker’s MAC address.
This enables the attacker to receive all the packets connected between the target host
and attacker in the LAN and after that, the attacker can get the information and
modify the packets flowing in the LAN.
They can get access to sensitive
data just like an authorized person can get access to their network.
The attackers
without any knowledge of the authority can extract sensitive information.
There are
generally two types of countermeasures to notice the attack: detection and
prevention systems.
Detection systems detect the attack by sounding an alarm when
an attack is detected and prevention systems try to prevent or stop the attack from
happening.
There are generally different types of attacks that are encouraged by
ARP Spoofing to attack the ARP and they are Dos attack, MITM attack,
MAC flooding, MAC duplicating, MAC address spoofing, session hijacking, etc.
To make the attack successful different types of attacking tools are
used which are listed below in detail.
Tools used for ARP Spoofing Attack
ARPwner
ARPwner is a tool that is used for ARP poisoning and DNS poisoning attacks.
It
has a simple GUI and a plugin system to filter the information gathered.
It
also consists of an implementation of SSLtrip and is fully coded on python and on
GitHub, which can be modified according to the need of attackers.
This tool was
developed by Nicholas Trippar at BlackHat USA in 2012.
Arpoison
Arpoison is a network analyzer that sends ARP packets to/from specified MAC and
IP addresses.
It was created by Steve Buer who developed this tool to
analyze Ethernet traffic inside a local network using a switch.
This tool sends custom
ARP packets and bogus ARP replies to the local network.
Ettercap
Ettercap is an efficient tool for man-in-the-middle attacks on LAN.
It is responsible for
sniffing live connections, content filtering, and different other tricks.
It includes
different features for network and host analysis and also supports active and passive
separation of many protocols even the ciphered ones.
It is capable of performing
attacks against the ARP protocol. It can infect, replace and delete data in a
connection and captures passwords for different protocols like FTP, HTTP, POP,
SSH1, and many others.
It acts as a Swiss army knife for ARP poisoning and network
sniffing. It consists of filters and plug-ins which can perform all sorts of network
tasks.
Ettercap can run on Linux, BSD, Mac OS X, and Windows XP/2003/2007/2008
and also can work on wireless (802.11) and wired LANs.
Dsniff
It is a combination of password sniffing and network traffic analysis tool commonly
known as packet sniffer which was developed by Dug Song to analyze
different application protocols and extract appropriate information which can take
over various protocols like FTP, SMTP, HTTP, mailsnarf, urlsnarf, and passively
monitor sensitive information on a network for gathering interesting data like
passwords, e-mail IDs, logs, etc.







0 Comments
Feel Free To Ask Any Queries?